Two authors of books about te Tiriti o Waitangi discuss the modern relevance of the nation’s most important document and shifting attitudes towards it, despite pushback from the government.
We recently shared the stage for a public kōrero on te Tiriti o Waitangi. The event, held during Matariki as part of the Tāmaki Untold series, filled the Whare Wānanga. People stayed after to talk. They asked thoughtful, sometimes difficult questions as they connected over cups of tea.
We’re seeing this kind of energy across the country. People are showing up not to argue or feel guilty – but to learn.
What makes that so striking is how few New Zealanders were ever taught the basics about te Tiriti. That’s not an individual failing, it’s a systemic one. Some of the people in government who speak most confidently about te Tiriti may know less than the average person in the audience.
That’s why we sometimes need to start from the beginning.
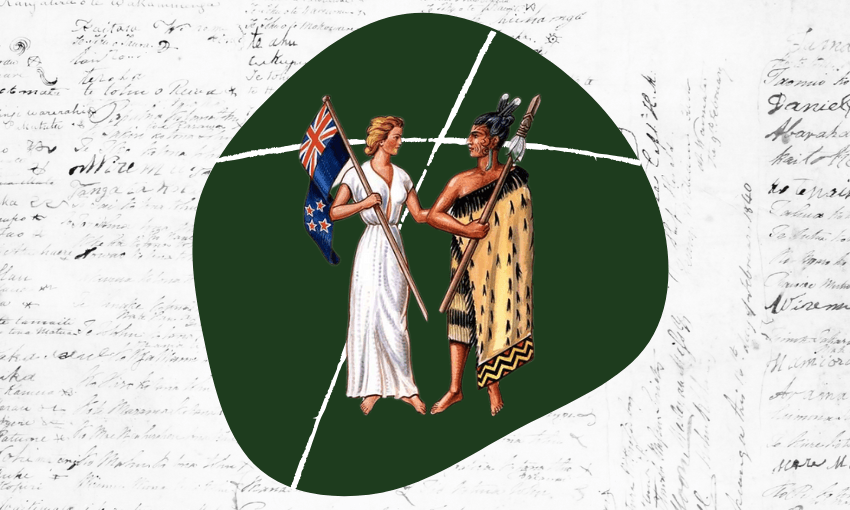
One of the questions Roimata was asked at our talk was: “Which is the authoritative document – te Tiriti or the Treaty?” It’s a common and important question.
She laid it out like this:
Māori discovered Aotearoa. Moriori discovered Rēkohu. They held tino rangatiratanga – complete authority – over their lands and lives. That’s not ancient history; that’s most of our history.
By 1840, Queen Victoria’s representatives wanted the exclusive right to buy land and a way to control British settlers. They promised protection and partnership. These were the terms discussed and recorded in te Tiriti o Waitangi, in te reo Māori. It reaffirmed Māori authority, echoing He Whakaputanga o te Rangatiratanga o Nu Tireni, the 1835 Declaration of Independence.
But a different version – the Treaty of Waitangi – was written in English, asserting that the Queen would have “sovereignty” – the power to make laws over everyone, including Māori. That was never discussed or agreed.
It’s important to set this all out when giving the short answer: only te Tiriti was agreed to, so only te Tiriti can be authoritative. Still, since 1840, the Crown has acted on the English version, using it to justify a flood of laws that have harmed Māori and enabled the loss of more than 60 million acres – nearly 97% of Māori land.
When people hear this for the first time, they’re often stunned. Sometimes there are tears. But when people are met with compassion rather than shame, they lean in. They keep learning. They tell their friends. And they begin to expect better from our institutions.
We’ve both seen this shift up close. Avril met a woman after a talk who shared that her group was about to sign an MOU with their local hapū. She has been hosted by treaty education groups, who have been working in their communities, educating, leading protest actions and building networks for years
These efforts are part of a growing nationwide movement. The commitment to te Tiriti is real – and it predates this government and will outlast it. Today, there are more tauiwi who outwardly support te Tiriti than ever before.
And what’s most heartening is that this movement is grounded in hope. At a time when public conversations are often dominated by fear, misinformation or division, we are generally seeing the opposite in our communities: courage, curiosity and kindness.
In town halls, classrooms, marae and boardrooms, it’s ordinary people – not politicians – who are stepping up. They’re asking questions, challenging old assumptions, and imagining a future where Te Tiriti isn’t a source of tension, but a foundation for justice, understanding and shared strength.
It takes courage to admit you were never taught this history. It takes hope to believe things can be different. And it takes both to stay in the room, keep learning and take action.
In workplaces too, change is continuing. Despite government reversals, many organisations are choosing to keep investing in Tiriti education, co-designing projects with Māori partners, and ensuring staff have a basic understanding of tikanga and pronunciation as part of respectful engagement.
This matters. Non-Māori have a critical role to play – not just in backing Māori-led initiatives, but in educating our own communities, challenging our institutions and supporting the enactment of tino rangatiratanga in practice.
Yes, people still get nervous. Some worry about being tokenistic. Others fear making mistakes or overstepping. But the reality is that mistakes are inevitable in any learning journey. The key is to treat them as part of the process, not a reason to pull back.
Being useful looks different in different contexts. Sometimes it means stepping back and letting Māori leadership guide the kaupapa. Other times, especially where there are few Māori voices in a space, it means stepping up – but doing so under the direction of Māori colleagues and communities.
In the end, it’s about relationships. Te Tiriti was always meant to be a partnership – a mutually beneficial agreement between peoples. That vision still exists. Māori haven’t withdrawn the invitation. The door is still open and we’re seeing more and more people walk through it.
That’s what gives us hope. The future of this country will not be shaped solely by whoever is in power at any given moment. It’s being shaped every day by teachers, parents, kaumātua, rangatahi, social workers, union delegates, health workers, and neighbours – people who are choosing honesty over defensiveness, and connection over fear.
New Zealanders are ready to engage – if the facts are made accessible. We know that once people begin to understand, they often want to act. Hope grows fastest where knowledge replaces silence. The momentum is already here. And if it continues, the future of this country – grounded in te Tiriti – could be brighter than many dare imagine.
The full kōrero is available to stream now on Soundcloud.